Climate models warn of more extreme weather events as the world’s ocean surface temperature hits record high
Climate change is not a vague and distant threat anymore, it is happening now, and its consequences are becoming more severe and frequent with each passing day. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and natural disasters have become commonplace worldwide. According to the latest reports from around the world, climate change is wreaking havoc on the global weather system, and the news paints a bleak picture of what’s to come.
Examples of these are already all around us. The U.S. state of California has been relentlessly hit by severe weather conditions, including heavy rain, strong winds, and thick snow, over the past three months. The state was previously facing a drought, but these recent events have led to devastating floods, and blizzards that have paralyzed the region, and numerous deaths.
Recently released data indicates that the state has received the most significant snowpack on record. This has prompted discussions with atmospheric and climate scientists, who shed light on the factors driving the surge in wet weather and how the state could be affected by a warmer future.
Add to this scientists’ warning on devastating tornadoes that have ripped through parts of the eastern and southern US could be a sign of the damage that will become more common due to global heating. Over a period of two weeks, more than 50 people have lost their lives due to tornadoes and thunderstorms, with the latest storm system causing widespread destruction in states such as Alabama, Illinois, Mississippi, Tennessee, and Arkansas.
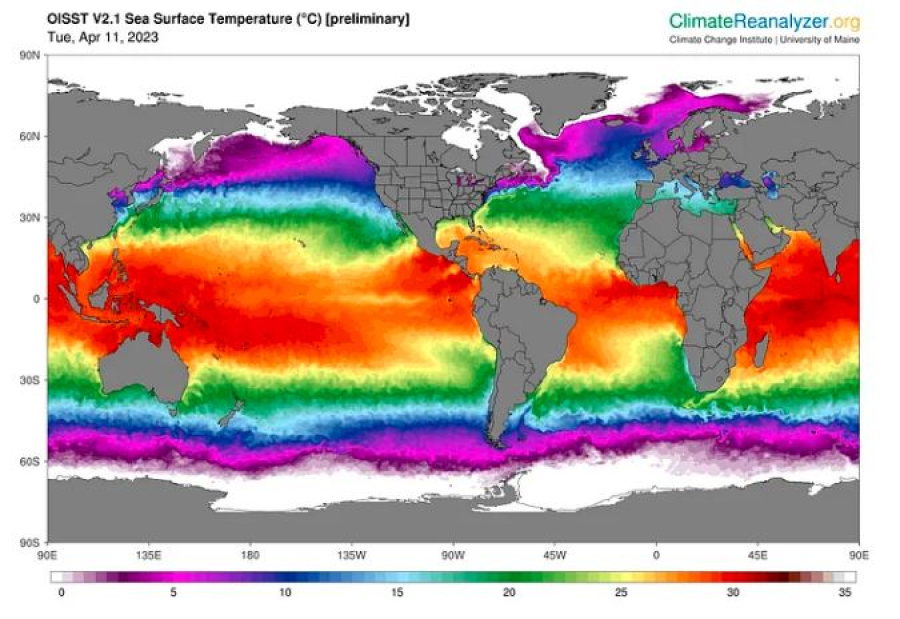
And this is just the United States, many other countries are facing similar weather-related catastrophes like the dry European winter drying canals in Venice and the African coast being hit by the longest-lasting tropical cyclone. US government data has now indicated that the temperature of the world’s ocean surface has reached a record high since the beginning of satellite records, leading to marine heatwaves across the planet.
According to preliminary data released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the average temperature at the ocean’s surface has been 21.1C since the start of April, surpassing the previous record of 21C set in 2016 (figure above). Climate scientists warn that this is a concerning trend and could have severe consequences for marine ecosystems and the planet as a whole.
The oceans’ temperature is a particular cause of concern, with recent reports indicating that the world’s ocean surface temperature is headed off the charts. The oceans absorb a significant amount of the heat that is trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere by greenhouse gases. The rising ocean temperatures are not just a threat to marine life and habitats but also have serious implications for human health and food security.
And this is where it makes it scary, all these events are interconnected. Hotter oceans not only have a limited capacity to absorb atmospheric heat, but they also provide more energy for storms, as well as putting ice sheets at risk and pushing up global sea levels, caused by salt water expanding as it warms. Thus the gigantic atmospheric rivers that poured down over California and devastating tornadoes over the mid-western U.S.
And talking about ice sheets, Global warming is accelerating the melting of ice in Antarctica, and the increased amount of freshwater flooding into the ocean is disrupting the flow of the Antarctic overturning circulation. As a result, a major ocean circulation that forms around Antarctica could be headed for collapse, risking significant changes to the world’s weather, sea levels, and the health of marine ecosystems.
Why is this important? You see, the Antarctic overturning circulation is a vital component of a worldwide system of currents that transport heat, oxygen, and nutrients across the planet (figured below). In the vicinity of Antarctica, frigid, saline water descends to depths surpassing 4,000 meters. The descent of the dense, oxygenated water stimulates the deepest movement of the overturning circulation. The water flows north, carrying oxygen and nutrients to the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic Oceans. A comparable process also takes place off the coast of Greenland.
However, indications suggest that the overturning circulation is decelerating, disrupted by the rising volume of meltwater originating from Antarctica, which is diluting the waters, making them less salty and, therefore, less dense, causing them to sink with reduced force. Additionally, the melting process is intensifying due to elevated levels of greenhouse gas emissions, predominantly from burning fossil fuels, that are heating up the atmosphere and oceans.

And now Climate scientists are also indicating an increased likelihood of an El Niño emerging later this year — a phenomenon characterized by Pacific Ocean warming that can heighten the chances of devastating weather events across the planet. Certain models are suggesting the potential emergence of an extreme, or “super El Niño,” later this year. This variety is distinguished by exceptionally high temperatures in a central area of the Pacific encircling the equator.
The previous super El Niño in 2016 was a contributing factor in driving global temperatures to unprecedented levels, exacerbated by human-induced global warming that triggered floods, droughts, and epidemics. In a recent report, the Bureau of Meteorology in Australia stated that all seven models it evaluated, including those from weather bureaus in the US, Japan, and the UK, indicate that ocean surface temperatures will surpass the El Niño threshold by August.
Needless to say, the latest news from around the world paints a grim picture and highlights the urgent need for action to mitigate the effects of climate change and transition to a more sustainable future. Governments, corporations, and individuals all have a role to play in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adopting sustainable business practices, and reducing our environmental footprint. It is time for us to take action to secure the future of our planet.
Faisal Khan / Medium